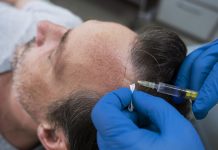
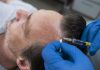
When most people hear the word Botox, they immediately think of its various cosmetic uses—specifically reducing the appearance of fine lines, wrinkles and the other signs of aging. This only makes sense as Botox is one of the most popular non-invasive cosmetic procedures performed, and thousands upon thousands of people regularly undergo Botox injections to help fight against the signs of aging.

However, the truth is that Botox has only been used for these cosmetic purposes since the early 1990s, whereas doctors have been using Botox injections for a number of other medical purposes since the late 1960s. Even if these injections are now more commonly used for cosmetic reasons, Botox can still provide a wide number of other medical benefits.
What is Botox?
The name Botox comes from the fact that these injections use a small amount of botulism toxin. Specifically, they use a toxin created by Clostridium botulinum bacteria. This toxin is generally considered to be the world’s most deadly poison. One gram is capable of killing more than 5.5 million people, and one pound of Botox would be enough to wipe out the entire human population. Despite the fact that it is extremely toxic, Botox is mostly harmless when used in extremely small dosages and can actually provide numerous medical benefits.
Non-Cosmetic Medical Uses of Botox
As a neurotoxin, Botox works by interfering with nerve signals, preventing them from reaching the muscles and thus basically paralyzing the muscle tissue. When Botox is injected into the face, it prevents the muscles from contracting and makes them less stiff, which helps to reduce or fully eliminate the appearance of wrinkles. These same properties allow Botox to also be an effective treatment for a range of other medical issues.
For instance, Botox has long been used to help patients treat problems with eyelid spasms (blepharospasm), hemifacial spasms and severe spasms in the neck or shoulder muscles (idiopathic rotational cervical dystonia). Botox is also often used in patients who have suffered a stroke to help treat spasms of the upper limbs. By paralyzing the muscles, Botox helps to eliminate the spasms.
In addition, Botox can also be used to help provide relief for patients suffering from severe chronic migraines and is also often used to treat patients with excessive sweating. Botox injections can also be used to treat patients with crossed eyes (strabismus), and it can even be used to relieve issues with urinary incontinence caused by overactive bladder-wall muscles.
Although all of the above are the only approved medical uses, it is also used for a number of off-label treatments that have yet to be officially approved.
How Does Botox Work?
Botox is typically injected directly into the muscles, where it will then begin blocking nerve signals from reaching the muscles. However, the effects of the injection are not immediate, and it usually takes anywhere from one to three days before it finally provides the desired results. In most cases, the effects of the injection will last for anywhere from two to four months—after which it becomes necessary to undergo an additional injection. This is true no matter whether the injections are being used for cosmetic or medical purposes.
Botox prices in Australia show that the treatment is generally becoming more and more affordable as time goes by, which also helps to explain why it is now the world’s most popular non-invasive cosmetic treatment. Although it definitely shouldn’t be considered a miracle treatment due to the fact that the results only last for a matter of months, the fact remains that Botox has a wide number of medical benefits. In some cases, Botox is the only treatment option that can provide relief, which means that it can be a huge benefit to a large number of people—not only those looking to reduce their wrinkles.