Every woman faces hormonal fluctuations. PMS, pregnancy, menopause, and many other factors can throw your hormones out of balance, but if you can’t pinpoint exactly what’s wrong, that’s a cause for concern.
Hormonal imbalance – what is it?
Hormones are substances secreted by the organs and tissues associated with the endocrine system. With blood, they enter the most remote parts of the body and deliver the information necessary for their well-coordinated life. In other words, they “tell” what, where and when to do and how quickly.
Hormones regulate a huge number of processes in the body: metabolism, sleep cycles, heart rate, mood, temperature – and this is just a small list of all that is under the strict supervision of hormones. Their work is often disrupted, and most often the reason for this is a decrease or increase in the amount of a particular hormone in the body.
Hormonal imbalance: how to recognize and prevent it
A person can both decrease and increase the level of insulin, cortisol, thyroxine, estrogen, progesterone, but each change seriously affects the general health condition.
If you cook dinner and add too much salt or pepper to it, your dish does not turn out the way it should have been – exactly the same thing happens to your body when a hormonal failure occurs.
How do you know that you are at risk?
Irregular menstrual cycle
For most women, the gap between periods is 21 to 35 days. If you notice that every month they come at different times or – worse – do not come at all, this may mean that your body either lacks certain hormones, or, conversely, their levels are too high. Most often, this is due to the ratio of the hormones progesterone and estrogen.
If you are 40 or older, the failure can be caused by the so-called perimenopause – the period before menopause or the last independent menstruation of the female body.
In general, an irregular cycle can be a symptom of severe problems with the health of the reproductive system. In such a situation, the best tactic of action is to contact a gynecologist, pass all the necessary tests and start treatment if necessary.
Sleep problems

If you need several hours to fall asleep, and this happens regularly, this may well point to a hormonal imbalance. Progesterone, a hormone secreted by the ovaries, plays a significant role in maintaining sound, deep sleep.
If its level drops, it can affect both the quality of sleep and the speed of its arrival. What’s more, low estrogen levels can lead to nightmares, so it’s important to get diagnosed early.
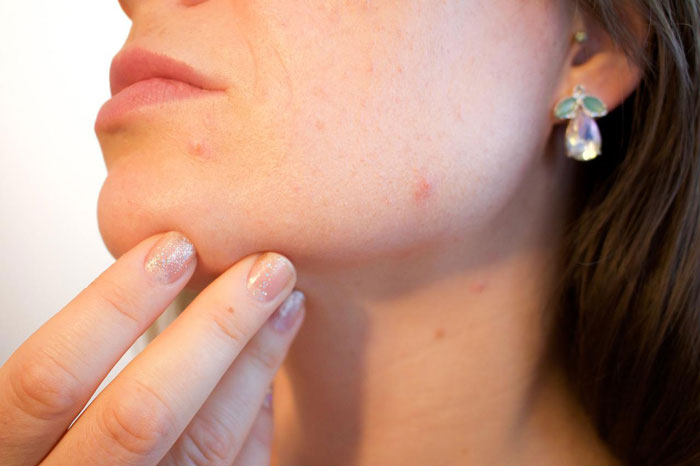
Chronic acne
Breakouts often happen during your period (or the days leading up to it), but if it plagues your skin consistently, it’s a sign of a serious hormonal imbalance.
An increased amount of androgens – “male” hormones present in both the male and female body – can cause the sebaceous glands to produce more hormones. They can also affect the function of cells around hair follicles. All this leads to rapid clogging of pores, and in the worst case, to the development of acne.
Memory fog
The influence of hormones on brain activity is still not fully understood. Still, it is known for sure that changes in the amount of estrogen and progesterone hormones can cause memory fogging. Some experts also agree that estrogen can affect neurotransmitters in the brain.
Well, in general, memory problems can be directly related to negative hormonal changes in the body, such as thyroid disease, for example.
Stomach problems
Our guts contain many receptors that respond to estrogen and progesterone. When these hormones become lower or higher than the normal level, you may notice significant changes in digestion.
Diarrhea, stomach pain, nausea – this can suddenly overshadow your well-being if the work of hormones is disrupted. If at the same time you observe frequent rashes and fatigue, then it’s time to contact a specialist.
Breast changes

Reducing the amount of estrogen – the main female sex hormone – can cause breast tissue to become less dense. But an increase in its amount can work opposite, which is not always positive: the breast tissue will gain density. In the process, there is a risk of cysts and other formations.
Rapid weight gain
If you feel sad or irritated, which often happens when estrogen levels drop, your appetite may kick in. A decrease in the amount of this hormone can lead to noticeable weight gain: it is known that if this happens with estrogen, this can also affect the performance of another hormone – leptin, which helps regulate food intake.
How to prevent hormonal failure?
Add polyunsaturated acids to your diet: omega-3 and omega-6 will help reduce appetite and the risk of obesity. These acids trigger leptin production, so they are unlikely to make you gain weight.
The next time you’re looking for a coffee or tea break, think about adaptogenic herbs. Adaptogen plants affect the body’s physiology, normalizing its internal processes, including the work of the hormone cortisol.
Taking probiotics will help maintain the balance of microflora and the normal ratio of “bad” and “good” bacteria. The more of the latter in the body’s intestines, the easier it is for people to process the food consumed. It has also long been proven that estrogen-related hormonal disruptions can be reversed with the help of probiotics, which replenish estrobolomas, the bacteria responsible for processing estrogens.
Vitamin D deficiency is one of the most common problems in the world. However, it has a lot more negative consequences than it might seem at first glance: vitamin D plays a decisive role in a number of bodily functions, including immune and anti-inflammatory reactions. A low level of this vitamin can lead to hypothyroidism – a lack of thyroid hormones and a decrease in the intensity of its work.
3-4 hours of sleep are critical for the body. With this amount of sleep, the body begins to experience real hormonal stress. There is an increase in the amount of the ghrelin hormone, which is responsible for appetite, and a simultaneous decrease in the leptin hormone, which is responsible for feeling full. It also leads to the risk of weight gain and poor metabolism. That is why normal sleep is one of the main components of health. If it is enough, the secretion of growth hormones increases in the body, which help to repair cells and produce new ones with greater intensity.